浅拷贝
浅拷贝:是指将一个对象复制到另一个变量中,但是只复制对象的地址,而不是对象本身。
也就是说,原始对象、和复制对象实际上是共享同一个内存地址的,如果修改了复制对象,原始对象也会改变。
如下图所示:
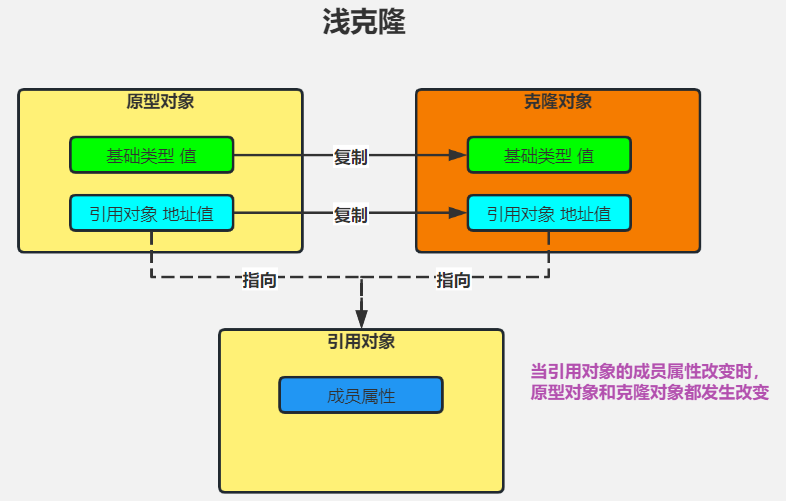
当引用对象的成员属性改变时,原型对象和拷贝对象都会发生改变。
看一个例子:
public class CopyTest {
static class Address {
String city;
Address(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
static class Person implements Cloneable {
String name;
Address address;
Person(String name, Address address) {
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
// 实现浅拷贝
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Address address = new Address("New York");
Person person1 = new Person("John", address);
Person person2 = (Person) person1.clone();
System.out.println("Person1 Address: " + person1.address.city); // 输出: New York
System.out.println("Person2 Address: " + person2.address.city); // 输出: New York
person2.address.city = "Los Angeles";
System.out.println("After changing person2's address:");
System.out.println("Person1 Address: " + person1.address.city); // 输出: Los Angeles
System.out.println("Person2 Address: " + person2.address.city); // 输出: Los Angeles
}
}
输出为:
Person1 Address: New York Person2 Address: New York After changing person2's address: Person1 Address: Los Angeles Person2 Address: Los Angeles
改变 person2 的 address 会为:”Los Angeles“影响 person1,因为它们共享同一个 Address 对象的引用。
深拷贝
深拷贝会创建一个全新的对象,并将原始对象中的所有属性、或元素都复制到新的对象中。
这个新对象不仅复制原始对象的所有非静态字段值,还会递归地复制所有引用类型字段所指向的对象,确保新对象和原对象之间没有共享的可变对象。
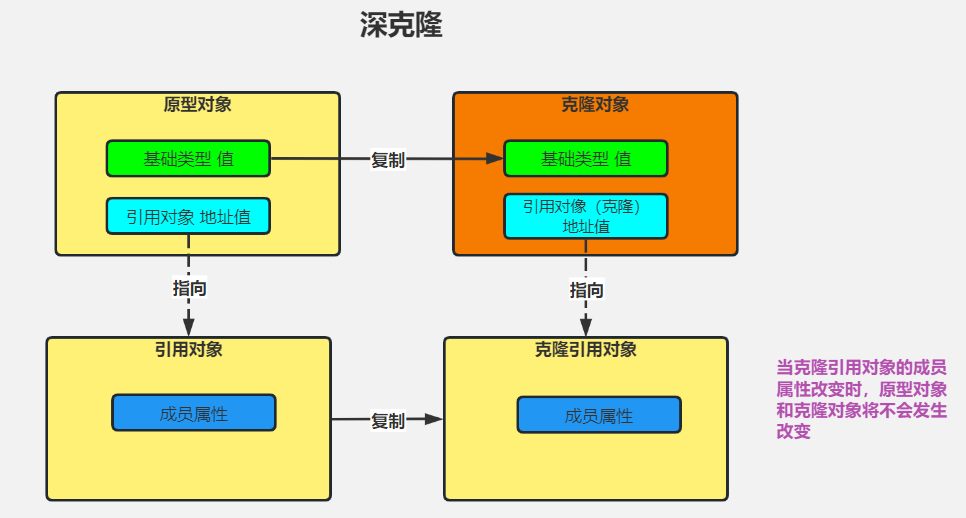
如果我们修改复制对象中的属性或元素,原始对象中对应的属性或元素不会受到影响。
看一个例子:
package com.mikechen.java.basis;
public class ShenCopyTest {
static class Address implements Cloneable {
String city;
Address(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
// 实现深拷贝
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return new Address(this.city);
}
}
static class Person implements Cloneable {
String name;
Address address;
Person(String name, Address address) {
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
// 实现深拷贝
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person clonedPerson = (Person) super.clone();
clonedPerson.address = (Address) this.address.clone();
return clonedPerson;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Address address = new Address("New York");
Person person1 = new Person("John", address);
Person person2 = (Person) person1.clone();
System.out.println("Person1 Address: " + person1.address.city); // 输出: New York
System.out.println("Person2 Address: " + person2.address.city); // 输出: New York
person2.address.city = "Los Angeles";
System.out.println("After changing person2's address:");
System.out.println("Person1 Address: " + person1.address.city); // 输出: New York
System.out.println("Person2 Address: " + person2.address.city); // 输出: Los Angeles
}
}
输出:
Person1 Address: New York Person2 Address: New York After changing person2's address: Person1 Address: New York Person2 Address: Los Angeles
Person 类的 clone 方法不仅调用 super.clone(),还显式地调用了 address 对象的 clone 方法,实现了深拷贝。
